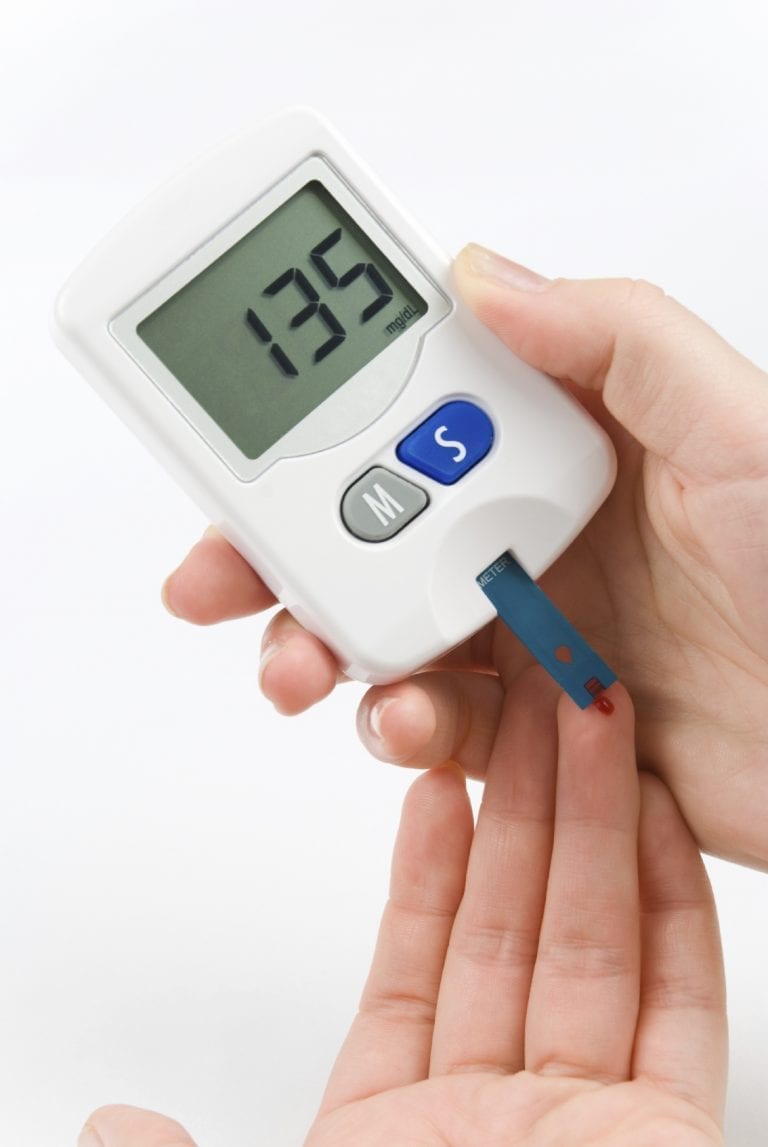
Gestational diabetes, or high blood sugar in pregnancy in a woman who has never had high blood sugar, is being diagnosed more often and in younger women.
Hormones produced by the placenta that help the baby develop also block the effect of the mother’s insulin. This means that pregnant women must make more insulin to keep their sugars in normal ranges. If the mother can’t produce enough insulin, her blood sugars rise, causing high blood sugar in her fetus, which can result in an overweight baby at birth.
Women with gestational diabetes are at risk for other complications such as pregnancy-induced hypertension. Although most women go back to normal after delivery, more than 50% eventually develop type 2 diabetes after having gestational diabetes in pregnancy. Those big babies are also more likely to develop diabetes. Treatment aimed at keeping your blood sugar as normal as possible and helps ensure a safe pregnancy and a healthy baby.





Comments are closed.